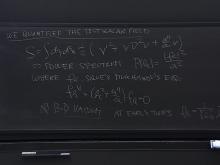Cosmologists at Perimeter Institute seek to help pin down the constituents and history of our universe, and the rules governing its origin and evolution. Many of the most interesting clues about physics beyond the standard model (e.g., dark matter, dark energy, the matter/anti-matter asymmetry, and the spectrum of primordial density perturbations], come from cosmological observations, and cosmological observations are often the best way to test or constrain a proposed modification of the laws of nature, since such observations can probe length scales, time scales, and energy scales that are beyond the reach of terrestrial laboratories.
Format results
-
17 talks-Collection NumberC18012
Talk
-

Charting Fundamental Interactions
Francesco Sannino CP3-Origins
-

Asymptotic safety with and without supersymmetry
Daniel Litim University of Sussex
-

-

Progress in constructing an Asymptotically safe Standard Model
Steven Abel Durham University
-

Cosmological non-Constant Problem
Niayesh Afshordi University of Waterloo
-

-

UV-complete relativistic field theories and softened gravity
Alberto Salvio Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa
-
Asymptotic safety of gravity-matter systems and effective universality
Manuel Reichert University of Southern Denmark
-
-
PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology (Smith)
15 talks-Collection NumberC17053Talk
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 1
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 2
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 3
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 4
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 5
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 6
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 7
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology - Lecture 8
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-
-
General Relativity for Cosmology (PHYS786/AMATH875) - Achim Kempf
24 talks-Collection NumberC17021Talk
-
General Relativity for Cosmology - Lecture 1
Achim Kempf University of Waterloo
-

General Relativity for Cosmology - Lecture 2
Achim Kempf University of Waterloo
-

General Relativity for Cosmology - Lecture 3
Achim Kempf University of Waterloo
-

General Relativity for Cosmology - Lecture 4
Achim Kempf University of Waterloo
-

General Relativity for Cosmology - Lecture 5
Achim Kempf University of Waterloo
-

General Relativity for Cosmology - Lecture 6
Achim Kempf University of Waterloo
-
-

General Relativity for Cosmology - Lecture 8
Achim Kempf University of Waterloo
-
-
Bounce Scenarios in Cosmology
16 talks-Collection NumberC17024Talk
-

Welcome and Opening Remarks
-
Steffen Gielen University of Sheffield
-
Neil Turok University of Edinburgh
-
-

Bounce in Loop Quantum Cosmology and its Implications
Abhay Ashtekar Pennsylvania State University
-

Observable Consequences of a Bounce
Ue-Li Pen Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics (CITA)
-

Challenges for Bouncing Cosmologies
Robert Brandenberger McGill University - Department of Physics
-

Emergent bouncing cosmology from quantum gravity condensates
Edward Wilson-Ewing University of New Brunswick
-

Discussion Session 2
-
Angelika Fertig TotalEnergies (France)
-
Steffen Gielen University of Sheffield
-
Elizabeth Gould Arthur B. McDonald Canadian Astroparticle Physics Research Institute
-
-

-

-
-
PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology (Smith)
14 talks-Collection NumberC17012Talk
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 1
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 2
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 3
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-
PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 4
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 5
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 6
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 7
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology - Lecture 8
Kendrick Smith Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-
-
PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Kubiznak)
15 talks-Collection NumberC17003Talk
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 1
David Kubiznak Charles University
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 2
David Kubiznak Charles University
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 3
David Kubiznak Charles University
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 4
David Kubiznak Charles University
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 5
David Kubiznak Charles University
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 6
David Kubiznak Charles University
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 7
David Kubiznak Charles University
-

PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Review) - Lecture 8
David Kubiznak Charles University
-
-
Time in Cosmology
14 talks-Collection NumberC16016Talk
-

Welcome and Opening Remarks
-
Marina Cortes Institute for Astrophysics and Space Sciences
-
Lee Smolin Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
-
Neil Turok University of Edinburgh
-
-

-

The origin of arrows of time II
-
Sean Carroll California Institute of Technology (Caltech) - Division of Physics Mathematics & Astronomy
-
Marina Cortes Institute for Astrophysics and Space Sciences
-
Tim Koslowski Technical University of Applied Sciences Würzburg-Schweinfurt
-
-

The origin of arrows of time II cont.
-
Sean Carroll California Institute of Technology (Caltech) - Division of Physics Mathematics & Astronomy
-
Marina Cortes Institute for Astrophysics and Space Sciences
-
Tim Koslowski Technical University of Applied Sciences Würzburg-Schweinfurt
-
-

Testing time asymmetry in the early universe
-
Brian Keating University of California, San Diego
-
Andrew Liddle University of Lisbon
-
Richard Muller University of California, Berkeley
-
-

The fate of the big bang
-
Abhay Ashtekar Pennsylvania State University
-
Neil Turok University of Edinburgh
-
-

Time as Organization – Downward Caustation, Structure and Complexity I
Barbara Drossel Technische Universität Darmstadt
-

Time as Organization – Downward Caustation, Structure and Complexity II
-
Stuart Kauffman Santa Fe Institute
-
George Ellis University of Cape Town
-
-
-
Cosmological Frontiers in Fundamental Physics 2016
21 talks-Collection NumberC16009Talk
-

Welcome and Opening Remarks
PIRSA:16060006 -

Dark matter phenomenology across cosmic times
Yacine Ali-Haimoud Johns Hopkins University
-
-

-

-

A new probe of primordial magnetic fields at high redshift
Vera Gluscevic University of Southern California
-

Turbulent gravity in asymptotically AdS spacetimes
Stephen Green University of Nottingham
-

Black hole ringdown and quasinormal modes
Aaron Zimmerman The University of Texas at Austin
-
-
Feedback over 44 Orders of Magnitude: From Gamma-rays to the Universe
22 talks-Collection NumberC16004Talk
-

30000 foot view of blazar heating
Christoph Pfrommer Universität Heidelberg - Institut für Theoretische Physik
-

The basics and not-so-basic physics of beam plasmas
Antoine Bret University of Castilla-La Mancha
-

The Basics of the Gamma-ray Sky: current observational status and future perspectives
Jim Hinton Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics - Albert Einstein Institute (AEI)
-

The thermal state of the intergalactic medium and its effect on galaxy formation
Matthew McQuinn University of Washington
-

Models of Galaxy formation: Current constraints on the star formation history and feedback
Hojun Mo University of Massachusetts Amherst
-

Nonlinear Plasma Instabilities
Philip Chang University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
-

-

-
-
Superluminality in Effective Field Theories for Cosmology
17 talks-Collection NumberC15019Talk
-

-

Causal structures in Massive gravity and Gauss-Bonnet gravity
Keisuke Izumi National Taiwan University
-

-

-

-

-

Causality constraints and the lightcone
Timothy Hollowood Swansea University
-

-
-

Axion-dilaton interactions in the dark sector
Adam Smith University of Sheffield
-

Forecasting LSST Cosmology: Building Pipelines in the Era of Systematics
Niko Sarcevic Newcastle University
-
Asymptotic Safety in a Dark Universe
17 talks-Collection NumberC18012The asymptotic safety paradigm is currently emerging as a highly promising idea for Beyond-Standard-Model physics with key progress in asymptotically safe quantum gravity and asymptotically safe matter models. The last years have seen not only the development of asymptotically safe gravity-matter models but also the discovery of asymptotically safe beyond Standard Model matter models that are under control in perturbation theory. New exciting avenues in (astro) particle physics are now waiting to be explored. For example although the nature of dark matter is a long-standing riddle it is a fact that experimental searches have so far not provided any direct clues but have instead come up with ever more stringent constraints on theoretically preferred regions of parameter space for dark-matter-models. Thus the key to unraveling this riddle could be a new theoretical paradigm to guide model builders. This workshop aims at exploring whether asymptotic safety can be a candidate for this new paradigm. We aim to bring together experts on phenomenological models and quantum gravity to probe both the theoretical viability and empirical signatures of asymptotically safe extensions of the standard model that include gravity. To facilitate a highly productive meeting that can trigger new collaborations each talk will be followed up by 15-20 minutes discussion time. Further each day of the workshop will feature a dedicated discussion session. Participants will be encouraged to contribute questions for the discussion both before as well as during the workshop. The last day of the workshop will conclude with a roadmap discussion during which all participants will be given the opportunity to propose concrete suggestions for follow-up work that might lead into future joint projects.
-
PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology (Smith)
15 talks-Collection NumberC17053PSI 2017/2018 - Cosmology (Smith) -
General Relativity for Cosmology (PHYS786/AMATH875) - Achim Kempf
24 talks-Collection NumberC17021General Relativity for Cosmology (PHYS786/AMATH875) - Achim Kempf -
-
PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology (Smith)
14 talks-Collection NumberC17012PSI 2016/2017 - Explorations in Cosmology (Smith) -
PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Kubiznak)
15 talks-Collection NumberC17003PSI 2016/2017 - Cosmology (Kubiznak) -
-
Cosmological Frontiers in Fundamental Physics 2016
21 talks-Collection NumberC16009Cosmological Frontiers in Fundamental Physics 2016 -
Feedback over 44 Orders of Magnitude: From Gamma-rays to the Universe
22 talks-Collection NumberC16004Feedback over 44 Orders of Magnitude: From Gamma-rays to the Universe
-
Superluminality in Effective Field Theories for Cosmology
17 talks-Collection NumberC15019Superluminality in Effective Field Theories for Cosmology -

Axion-dilaton interactions in the dark sector
Adam Smith University of Sheffield
Axion-dilaton models provide a well-motivated, minimal class of models for which kinetic interactions between multiple scalar fields and their predictions can be explored, in particular in late time cosmology. I will review this class of models and present the formalism we developed for studying kinetic interactions between rapidly oscillating axion fields and their dilaton partners on cosmological scales. -

Forecasting LSST Cosmology: Building Pipelines in the Era of Systematics
Niko Sarcevic Newcastle University
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory’s LSST promises unprecedented cosmological constraints, but achieving them requires more than just statistical power—it demands forecasting pipelines that can account for complex astrophysical systematics and modeling challenges on small scales. In this talk, I present work within the LSST Dark Energy Science Collaboration (DESC) to develop a modular forecasting framework that connects realistic data modeling with infrastructure built for extensibility and validation. Drawing on my role as forecasting group lead, I will outline key challenges in pipeline design, the role of validation in maintaining forecast credibility, and the use of good coding practices—such as modularization and model registries—to ensure long-term adaptability. I’ll close with a look at new directions, including forecasts at high redshift and multi-probe combinations, underscoring how thoughtful infrastructure enables reliable science in the LSST era.